Foot & Ankle
- Anatomy
- Conditions
- Procedures
What is the Normal Anatomy of the Foot and Ankle?
The foot and ankle are a complex joint involved in movement and providing stability and balance to the body. The foot and ankle consist of 26 bones, 33 joints, and many muscles, tendons and ligaments.
Bones of the Ankle
The ankle joint connects the leg with the foot and is composed of three bones: tibia, fibula and talus. The tibia or shinbone and fibula or calf bone are bones of the lower leg which articulate with the talus or ankle bone, enabling up and down movement of the foot.
Three bony bumps present on the ends of the tibia and fibula form parts of the ankle joint:
- The medial malleolus, formed by the tibia, is found on the inside of the ankle.
- Posterior malleolus, also formed by the tibia, is found at the back of the ankle.
- Lateral malleolus, formed by the fibula, is found on the outer aspect of the ankle.
Bones of the Feet
The foot acts as a single functional unit, but can be divided into three parts: the hindfoot, midfoot and forefoot.
The hindfoot forms the ankle and heel and is made up of the talus bone and calcaneus or heel bone. The heel bone is the largest bone in the foot.
The midfoot connects the hindfoot to the forefoot, and consists of one navicular bone, one cuboid bone, and three cuneiform bones. The navicular bone is found in front of the heel bone, and the cuneiform and cuboid bones are arranged in front of the navicular bone.
These bones are connected to five metatarsal bones of the forefoot, which form the arch of the foot for shock absorption while walking or running. The forefoot is also made up of the toes or digits, formed by phalanges, three in each toe, except the big toe, which has only two phalanges. The big toe has two additional tiny round sesamoid bones in the ball of the foot, which help in upward and downward movement of the toe.
Ankle and Foot Joints
There are 33 joints in the ankle and foot. They include:
- Hinge joints in the ankle, which allow flexion (bending) and extension
- Gliding joints found in the hindfoot, which allow gliding movements
- Condyloid joints found in the forefoot and toes, which allow the flexion (bending) and extension, adduction and abduction (sideward movement).
The joints of the foot and ankle provide stability and support the weight of the body, helping you to walk or run, and to adapt to uneven ground.
The joint surface of all bones of the ankle and foot are lined by a thin, tough, flexible, and slippery surface called articular cartilage, which acts as a shock absorber and cushion to reduce friction between the bones. The cartilage is lubricated by synovial fluid, which further enables smooth movement of the bones.
Soft Tissues of the Ankle and Foot
Our feet and ankle bones are held in place and supported by various soft tissues such as cartilage, ligaments, muscles, tendons and bursae.
Cartilage is the flexible, shiny, smooth tissue on the ends of bones that meet to form a joint. Cartilage provides cushioning between the bones allowing smooth movement.
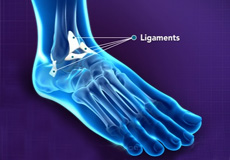
Ligaments are tough rope-like tissue that connect bones to other bones, and holds them in place providing stability to the joints. The plantar fascia is the largest ligament in the foot, originating from the heel bone to the forefoot, it extends along the bottom surface of the foot and is involved in maintaining the arch of the foot. The plantar fascia ligament stretches and contracts to provide balance and strength to the foot. Lateral ligaments on the outside of the foot and medial ligaments on the inside of the foot provide stability and allow up and down movement of the foot.
The foot is made up of 20 muscles, which help in movement. The main muscles include:
- Anterior tibial muscle: allows up and down movement of the foot
- Posterior tibial muscle: supports the arch
- Peroneal tibial muscle: controls movement on the outside of the ankle
- Extensors: enable the ankle to raise the toes just before stepping forward
- Flexors: stabilize the toes against the floor
- Smaller muscles are also present to help the toes lift and curl.
Tendons are soft tissues that connect muscles to bones. The largest and strongest tendon in the foot is the Achilles tendon, present at the back of the lower leg around the heel bone. Other tendons include peroneal and anterior and posterior tibialis.
Bursae
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that decrease friction between tendons and bone or skin. Bursae contain special cells called synovial cells that secrete a lubricating fluid.
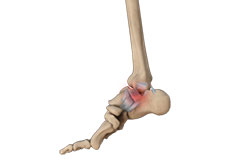
Ankle Sprain
A sprain is the stretching or tearing of ligaments, which connect adjacent bones and provide stability to a joint. An ankle sprain is a common injury that occurs when you suddenly fall or twist the ankle joint or when you land your foot in an awkward position after a jump. Most commonly it occurs when you participate in sports or when you jump or run on a surface that is irregular.
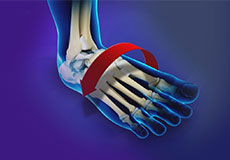
Ankle Instability
Ankle instability is a chronic condition characterized by a recurrent slipping of the outer side of the ankle. It usually results from repeated ankle sprains. It is generally noticed during movement of the ankle joint but can also occur during standing as well.
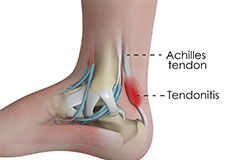
Achilles Tendinitis
Achilles tendinopathy is characterised by degeneration of the fibres of the Achilles tendon. This can occur either directly at the insertion of the tendon into the heel bone (insertional tendinopathy), or in an area approximately 3-10cm above the insertion (non-insertional tendinopathy).
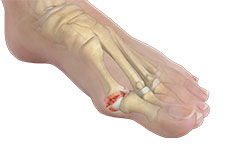
Stiff Big Toe (Hallux Rigidus)
Hallux rigidus is an arthritic condition characterised by stiffness and rigidity of the big toe. Arthritis of the foot commonly occurs at the big toe joint (1st metatarsophalangeal [MTP] joint). The condition can be quite painful as the big toe usually bends with every step you take.
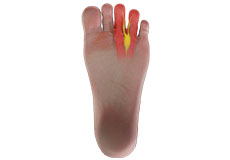
Morton's Neuroma
Morton’s neuroma refers to a nerve injury between the toes, usually the third and fourth toes, which causes pain and thickening of the nerve tissue. Compression or chronic irritation of this interdigital nerve is the main cause of Morton’s Neuroma. Excess pressure is exerted on the nerves due to the narrowing of the gap between the toe bones, causing thickening of the nerve tissue from scar tissue formation.
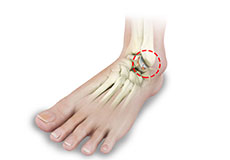
Foot and Ankle Arthritis
Arthritis is inflammation resulting from the degeneration of cartilage in the joint causing joint pain, swelling, and stiffness resulting in restricted movements. Arthritis of the foot and ankle joint can occur due to fractures, dislocation, inflammatory disease, or congenital deformity.
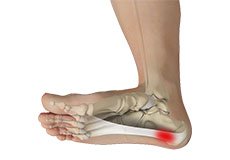
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis refers to inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that is present at the bottom of the foot. It runs from the heel bone to the toe and forms the arch of your foot. Plantar fasciitis is one of the most common causes of heel pain. It is most often seen in middle-aged men and women, but may also occur in those who are constantly on their feet.
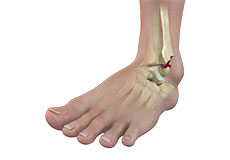
Ankle & Foot Fracture
Ankle injuries are very common in athletes and in people performing physical work, often resulting in severe pain and impaired mobility. Pain after ankle injuries can either be from a torn ligament and is called an ankle sprain or from a broken bone which is called an ankle fracture.
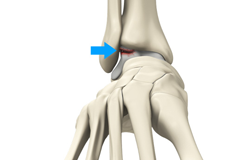
Ankle Injury (OCD)
The ankle joint is an articulation of the end of the tibia and fibula (shinbones) with the talus (heel bone). Osteochondral injuries, also called osteochondritis dissecans, are injuries to the talus bone, characterized by damage to the bone as well as the cartilage covering it. Sometimes, the lower end of the tibia or shinbone may also be affected.
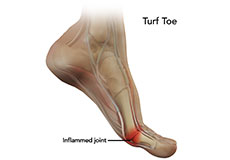
Turf Toe
Turf toe is an injury to the ligament at the base of the big toe. It is a painful condition which usually results from jamming the toe into the ground or excessive backward bending of the toe. As it is more common in athletes playing on artificial turf, especially those involved in field sports such as football, baseball and soccer, it is known as turf toe.
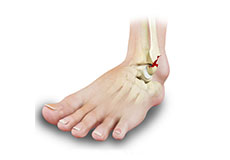
Foot Stress Fractures
A stress fracture is a small crack in a bone which occurs from an overuse injury. It commonly develops in the weight-bearing bones of the lower leg and foot. When the muscles of the foot are overworked, or stressed they are unable to absorb the stress and transfer it onto the bone, which cracks under the pressure.
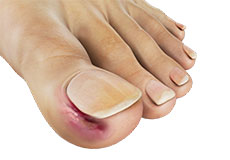
Ingrown Toenail
An ingrown toenail is a common and painful condition of the toe. It occurs when the side or corner of the nail grows inwards and penetrates the skin of the toe. Pain is often accompanied by swelling and redness. The big toe is affected most often.
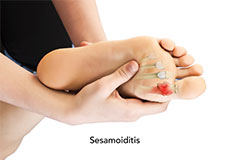
Sesamoiditis
Sesamoiditis is the inflammation of the sesamoid bones. The main cause of sesamoiditis is consistent pressure and tension applied over the foot. It is common in people who participate in potentially high intensity sports (runners) or jarring (jogging or boxing) activities.
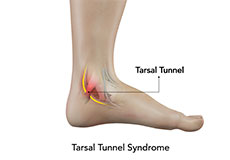
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
The tarsal tunnel is a gap that is formed between the underlying bones of the foot and the overlying tough fibrous tissue. Tarsal tunnel syndrome refers to a condition where the posterior tibial nerve that lies within the tarsal tunnel is compressed. The condition occurs when the tibial nerve is pinched.
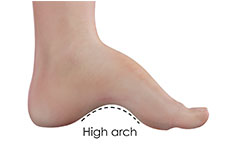
Cavus Foot Deformity
A cavus foot or a high-arched foot refers to a condition that can vary from a slightly high arch to a severe deformity. Cavus foot can lead to symptoms such as pain and instability. The condition may be inherited or associated with neurological disorders or other conditions.
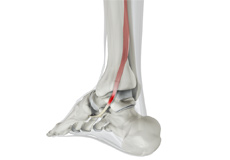
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
The posterior tibial tendon passes through the ankle to attach the calf muscle with the bones of the mid foot. It provides stability to the arch and supports the foot while walking. Inflammation or a tear of this tendon as a result of injury may cause dysfunction, leading to pain and the development of a flatfoot.
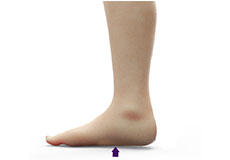
Adult (Acquired) Flatfoot
Adult acquired flatfoot is a very common condition that affects the feet and ankles of adult males and females. In people with adult acquired flatfoot, the arch of the foot falls or collapses. It can be a painful, sometimes debilitating condition. However, a painful flatfoot can usually be helped with braces or orthotics and other non-surgical treatments.
Ankle Arthroscopy
Ankle arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which an arthroscope, a small, soft, flexible tube with a light and video camera at the end, is inserted into the ankle joint to evaluate and treat a variety of conditions.
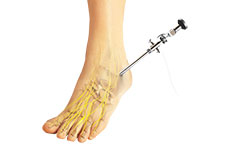
Syndesmosis With Tightrope Fixation
The ankle is made up of the tibia and fibula bones of the lower leg, and the talus bone of the foot. They are held together by ligaments, which provide strength and stability during movement.
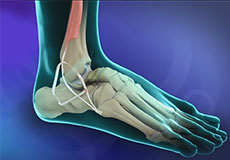
Ankle ligament Stabilisation
An ankle sprain is a common injury and occurs when you fall or suddenly twist the ankle joint or when you land your foot in an awkward position after a jump. It most commonly occurs when you participate in sports or when you jump or run on a surface that is irregular.
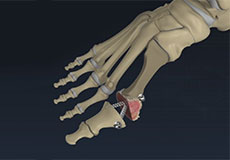
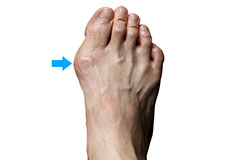
Bunion Surgery
A bunion, also known as hallux valgus, is bony prominence at the base of the big toe, which often results in pain, redness and rubbing in footwear. The first metatarsal bone abnormally angles outward towards the other foot from its joint in the midfoot. A bunion can change the shape of your foot, make it difficult for you to find shoes that fit correctly and worsen the symptoms if left untreated.
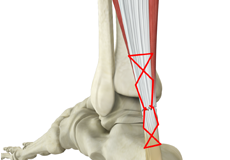
Surgery for a Torn Achilles Tendon
Tendons are the soft tissues connecting muscle to bone. The Achilles tendon is the longest tendon in the body and is present behind the ankle, joining the calf muscles with the heel bone.
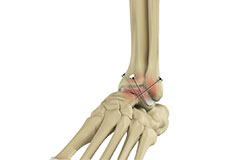
Ankle Fusion Surgery
Ankle fusion surgery also called, ankle arthrodesis, is the surgical fusion of bones that form the ankle joint. The ankle joint is formed by the tibia, talus, and the fibula bones.
The goal of ankle arthrodesis is to relieve pain in the affected joint. This is achieved by surgically eliminating the joint.
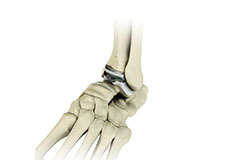
Ankle Joint Replacement
Ankle joint replacement, also known as total ankle arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure performed to relieve pain and immobility due to severe end stage arthritis that has not responded to non-surgical treatments. The goal of ankle joint replacement surgery is to eliminate your pain and increase the mobility of your ankle joint.

